
Leak-free hydraulic connections play a crucial role in ensuring operational efficiency. They help prevent costly downtime and reduce maintenance expenses. Additionally, avoiding leaks enhances safety and minimizes environmental risks. By choosing the right hydraulic fittings, such as hose fittings, hydraulic couplings, NPT fittings, and metric fittings, companies can improve system longevity and reliability.
Key Takeaways
- Leak-free hydraulic connections enhance operational efficiency and safety. They prevent costly downtime and reduce maintenance expenses.
- Choosing the right hydraulic fittings, like O-ring face seals, is essential for preventing leaks and ensuring system reliability.
- Regular inspections and maintenance can reduce unexpected hydraulic failures by up to 85%. Stay proactive to keep your systems running smoothly.
Types of Hydraulic Fittings

Hydraulic fittings are essential components in any hydraulic system. They connect hoses, tubes, and pipes, allowing fluid to flow efficiently. Understanding the different types of hydraulic fittings can help users select the right ones for their specific applications. Here’s a quick overview of some common fittings:
- Steel Hydraulic Fittings: Known for their strength and durability, these fittings come in both carbon and stainless steel options.
- Brass Fittings: These are popular due to their corrosion resistance and affordability.
- NPT (National Pipe Tapered): This fitting uses tapered threads to create a seal, making it a reliable choice for many applications.
- ORB (O-Ring Boss): Ideal for high-pressure situations, ORB fittings provide a secure seal that minimizes leaks.
- JIC (Joint Industry Council): These fittings feature a 37° cone for sealing and are widely used in various industries.
- ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal): Excellent for high-vibration environments, ORFS fittings help prevent leaks effectively.
When selecting hydraulic fittings, material choice is crucial. The right material can significantly impact the fitting’s performance and lifespan. Here’s a breakdown of some commonly used materials:
| Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Brass | Strong, durable, highly resistant to corrosion; works in -325° to 400° F | Small compression and threaded fittings; lower pressure situations. |
| Stainless Steel | High strength, durability, excellent corrosion resistance; -425° to 1200° F | Used in oil and gas offshore equipment, food manufacturing, chemical processing, marine, medical applications. |
| Carbon Steel | Durable, strong, high resistance to heat | Used in agricultural, industrial, and construction sectors; suitable for high pressure. |
Choosing the right material ensures that hydraulic fittings can withstand the specific conditions they will face. For instance, stainless steel is often preferred in corrosive environments due to its durability. On the other hand, brass fittings are suitable for lower pressure situations where corrosion resistance is essential.
O-ring Face Seals
O-ring face seals are essential components in hydraulic systems. They create a tight seal between different parts, preventing hydraulic fluid from leaking. When compressed, these seals adapt to the surfaces they touch. This adaptability is key; it blocks any gaps that could allow fluid to escape. By maintaining pressure within the system, O-ring face seals help ensure smooth operation.
Design and Functionality
The design of O-ring face seals is straightforward yet effective. They consist of a circular elastomer that fits into a groove on the fitting. When the fitting is tightened, the O-ring compresses, forming a seal. This design allows for a reliable connection that can withstand various pressures and temperatures.
O-ring face seals excel in extreme conditions. For instance, fluorocarbon (Viton®) O-rings can handle temperatures ranging from -15ºF to 400ºF. This broad temperature range makes them suitable for many applications, including those with high heat or cold exposure.
Advantages Over Other Fittings
O-ring face seals offer several advantages compared to traditional fittings like flare fittings. Here’s a quick look at some of the benefits:
| Design Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| The ORFS design avoids radial clearances, ensuring the O-ring doesn’t become pinched during installation. | This optimizes O-ring performance and enhances the seal’s lifespan. |
| Unlike JIC fittings that rely on a flared tube end for sealing, ORFS fittings seal on the flat face. | This design removes the possibility of over-torquing and damaging the flare, leading to a more resilient seal. |
| The flat face of the fitting makes metal-to-metal contact with the mating surface. | This ensures that there is no twisting or torque transferred to the O-ring, preventing premature wear and potential failure. |
These features make O-ring face seals a preferred choice in many hydraulic applications. They not only enhance the reliability of the connection but also contribute to the overall efficiency of the hydraulic system.
Installation Best Practices for Hydraulic Fittings
Installing hydraulic fittings correctly is essential for preventing leaks and ensuring system reliability. To achieve a leak-free connection, follow these best practices.
Tools and Equipment Needed
Before starting the installation, gather the following tools and equipment:
- Torque Wrench: This tool ensures precise torque control. It helps prevent over-tightening or under-tightening, which can lead to leaks or joint failures.
- Lubricant: Use a suitable lubricant for O-rings to enhance sealing.
- Cleaning Supplies: Keep the installation area clean to avoid contamination.
- Safety Gear: Always wear gloves and safety glasses to protect yourself during installation.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Follow these steps to install O-ring face seal fittings properly:
- Preparation: Clean the installation areas and inspect fittings for damage.
- O-ring Placement: Place the O-ring in the groove and apply lubricant.
- Insertion: Insert the male fitting into the female counterpart gently.
- Thread Engagement: Hand-thread the parts to avoid cross-threading.
- Tightening: Use a wrench to tighten according to torque specifications. A well-calibrated torque wrench minimizes the risk of catastrophic joint failure or component damage.
- Inspection: Visually check for misalignment or damage.
- System Testing: Conduct a pressure test to check for leaks.
- Maintenance & Regular Check-ups: Periodically inspect and replace O-rings as needed.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your hydraulic fittings are installed correctly, reducing the risk of leaks and enhancing system performance.
Maintenance Tips for Hydraulic Fittings

Maintaining hydraulic fittings is crucial for ensuring their longevity and performance. Regular inspections can help catch potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs or system failures. Here are some effective protocols for inspecting hydraulic fittings:
Regular Inspection Protocols
To keep hydraulic systems running smoothly, follow these inspection protocols:
- Daily Monitoring: Conduct essential checks to prevent 65% of hydraulic failures.
- Weekly Performance Analysis: Perform inspections that can extend component life by 45%.
- Monthly Maintenance: Schedule detailed checks to prevent 90% of major hydraulic failures.
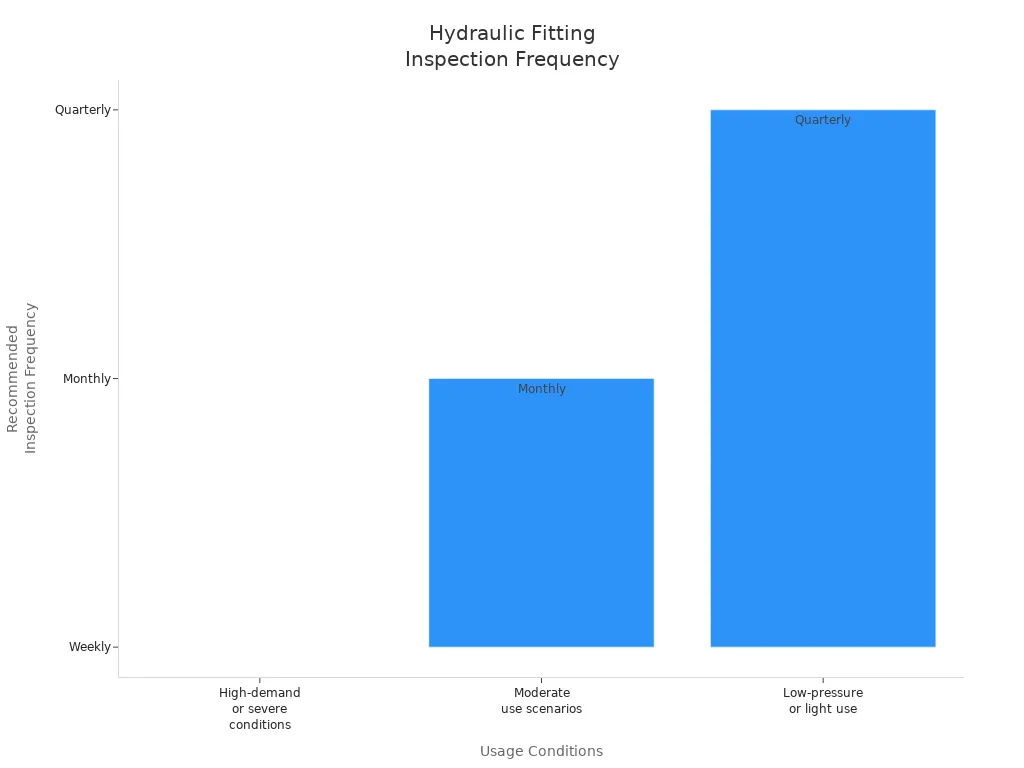
Here’s a quick reference table for inspection frequency based on usage conditions:
| Inspection Frequency | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Weekly | High-demand systems or severe conditions (e.g., high pressure, extreme temperatures) |
| Monthly | Standard for most hydraulic hoses in moderate use scenarios |
| Quarterly | Recommended for low-pressure or lightly used hoses |
Signs of Wear and Tear
Recognizing the signs of wear and tear in hydraulic fittings can save time and money. Here are some common indicators to watch for:
- Leaking Fittings: Look for visible hydraulic fluid around the fitting connections.
- Visible Cracks and Fractures: Check for fine lines or breaks in the fitting material.
- Corrosion and Rust: Identify rust or powdery residue on metal fittings.
- Deformation and Warping: Inspect for bent or distorted fittings.
- Worn or Damaged Threads: Examine threads for signs of wear or damage.
- Discoloration and Fading: Note any unusual color changes on the fitting surfaces.
- Loose or Misaligned Fittings: Check for movement or wobbling of fittings.
- Wear Marks and Abrasion: Look for scratches or grooves on the fittings.
The presence of hydraulic fluid outside the intended pathways often indicates a leak. This can stem from improper installation or wear on seals. Regular inspections can help catch these issues early, ensuring the system operates efficiently and safely.
By staying vigilant and following these maintenance tips, users can enhance the reliability of their hydraulic systems and prevent unexpected failures.
Troubleshooting Common Hydraulic Issues
Hydraulic systems can face various issues, with leaks being one of the most common problems. Identifying the source of these leaks is crucial for maintaining system efficiency and safety. Here’s how to pinpoint leak sources effectively.
Identifying Leak Sources
Several diagnostic methods can help locate leaks in hydraulic systems. Here’s a handy table summarizing these techniques:
| Diagnostic Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Imaging | Uses infrared cameras to detect temperature variations associated with hydraulic fluid leaks. |
| Ultrasonic Detection | Utilizes high-frequency sound waves to identify leaks in hydraulic systems. |
| Dye Penetrant Testing | Applies a colored dye to surfaces to identify leaks by seeping into cracks. |
| Visual Testing | Involves checking for visible signs of leaks, such as drips or wet surfaces. |
| Bubble Testing | Uses surfactants or water to detect gas leaks by observing bubble formation. |
| Pressure Change Testing | Measures pressure drop in a pressurized system to identify leaks. |
| Mass Spectrometry Testing | Detects trace amounts of leaked gas using a mass spectrometer, often with helium as a surrogate. |
Using these methods, technicians can quickly identify where leaks occur. For instance, dye penetrant testing is particularly effective. When technicians add fluorescent dye to hydraulic fluid, it glows bright yellow under UV light, making leak locations easily visible. This method can even detect small leaks that other techniques might miss.
Solutions for Common Problems
Once technicians identify the leak source, they can implement effective solutions. Here are some common strategies for repairing leaks in O-ring face seal fittings:
- Inspect the O-ring: Check for visible damage and ensure it is seated correctly. If there’s any doubt about its condition, replace the O-ring.
- Use compatible lubricants: Select a lubricant that works well with both the O-ring material and the hydraulic fluid. This prevents chemical breakdown.
- Tighten fittings properly: Ensure the fitting is tightened to the correct torque. If leaks persist, inspect and replace the O-ring as necessary.
Additionally, replacement intervals for hydraulic fittings can vary based on system pressure and usage. Technicians should follow manufacturer guidelines for replacement intervals, especially when dealing with high-pressure systems. Signs that indicate the need for replacement include persistent leaks, visible damage, and unusual system behavior.
By following these troubleshooting steps and solutions, technicians can effectively manage hydraulic issues, ensuring systems operate smoothly and efficiently. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to leaks can save time and resources in the long run.
Choosing the right hydraulic fittings is crucial for system efficiency. For example, NPT threads seal pipes effectively, while O-ring face seals prevent leaks, ensuring reliability. Regular maintenance is key; studies show that proactive practices can reduce unexpected failures by up to 85%. So, keep those systems running smoothly!
Post time: Sep-08-2025
