
Hydraulic hose connectors play a crucial role in factory operations. Industry leaders like Eaton Corporation and Parker Hannifin use advanced materials, such as stainless steel pipe fittings and stainless steel fittings, for reliability. Factories require connectors that withstand high pressure, with stainless steel braided hose options meeting strict safety and performance standards.
Key Takeaways
- Choose hydraulic hose connectors that match your system’s pressure, material, and compatibility needs to ensure safety and prevent leaks.
- Different connector types like JIC, SAE, ORFS, NPTF, NPSM, and BSP offer unique strengths suited for specific factory applications and environments.
- Follow proper installation steps and regular inspections to reduce downtime, extend equipment life, and keep hydraulic systems running smoothly.
Key Criteria for Selecting a Hydraulic Hose Connector
Pressure Rating
A hydraulic hose connector must handle the pressure demands of factory systems. Industry standards like SAE J517 and ISO 1436 set the rules for construction, testing, and performance.
- Hydraulic pressure testing, burst testing, and impulse testing check how connectors perform under stress.
- Working pressure shows the safe limit for daily use, while burst pressure marks the point of failure.
- Safety factors, often between 3 and 4, give extra protection.
- The connector’s design, material, and environment all affect its pressure rating.
Meeting these standards helps factories avoid leaks and failures.
Material Durability
Material choice affects how long a connector lasts.
| Hose Material | Lifespan Estimate | Durability Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber Hoses | 5 to 10 years | Moderate abrasion resistance; can be damaged by UV and chemicals |
| Thermoplastic Hoses | 3 to 7 years | Good chemical resistance; lighter but less tough in harsh settings |
| Metal Hoses | 10+ years | Very durable and wear-resistant; less flexible |
Threaded couplings often last longer than other types, showing no damage after millions of cycles. Factories that use reinforced hoses see less downtime and better impact resistance.
Compatibility and Standards
Factories need connectors that fit their systems and fluids. Testing methods like burst and impulse tests help set safety margins and life expectancy. ISO certifications and SAE standards show that a connector meets global quality rules.
Proper thread type, seat angle, and fitting design prevent leaks and ensure a good match.
Manufacturers who follow these standards make connectors that work well in modern factories.
Sealing Method
Sealing methods keep hydraulic systems leak-free. New designs, such as wedge-buckled copper seals with steel rings, have proven effective even in high-temperature, high-pressure settings.
Studies show that adjusting the wedge angle in sealing joints improves leak prevention.
These advances help factories maintain safe and reliable operations.
Installation Type
Installation affects both safety and maintenance.
- Switching from threaded fittings to hydraulic flanges can cut maintenance downtime by 30%.
- Flanges handle pressure and vibration better, making them safer and easier to install.
- Good installation practices include checking parts, placing O-rings correctly, and tightening bolts to the right torque.
- Workers should always depressurize systems and use protective gear.
Comparative Review of Top Hydraulic Hose Connector Types

JIC (Joint Industry Council) Connectors
JIC connectors use a 37-degree flare design. This design creates a strong, leak-proof seal under high pressure. Many factories choose JIC connectors for their durability and reliability.
- JIC connectors handle high pressure, making them suitable for aerospace, defense, and heavy machinery.
- They resist vibration, which helps prevent leaks and damage.
- These connectors use imperial (UNF) threads, common in North American equipment.
- JIC connectors follow SAE J514 standards, ensuring consistent quality.
- Stainless steel and brass options provide corrosion resistance.
- Workers find JIC connectors easy to install with standard tools, which can reduce maintenance time.
JIC connectors improve system efficiency by reducing maintenance needs and offering reliable performance in tough environments.
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) Connectors
SAE connectors meet strict standards for high-pressure hydraulic systems. The SAE J1926 standard guides their design and testing.
SAE connectors go through several tests to prove their strength and safety:
| Test Type | Description | Standards Referenced |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue Testing | 1,000,000 to 2,000,000 cycles to check endurance under repeated pressure | NFPA/T2.6.1 R1-1991, NFPA T2.6.1R2-2000 |
| Burst Pressure Test | Hydrostatic pressure testing to failure | ISO 1436-1:2001, SAE J343 4.4 MAR 1999 |
| Proof Test | Checks pressure resistance at rated pressures | SAE J343 4.2 MAR 1999 |
| Endurance Test | Long-term durability under cyclic pressure | NFPA/T2.6.1 R1-1991 |
| Pressure Test | Confirms plug integrity under internal and external hydrostatic pressures | Fluid Power Institute protocols |
These tests show that SAE connectors can handle high pressure and temperature. Factories trust them for leak-free and reliable performance. SAE connectors help keep hydraulic systems safe and efficient.
ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) Connectors
ORFS connectors use an O-ring to create a face seal. This design stops leaks, even in extreme conditions.
- Rocket engine systems use ORFS connectors to keep seals tight at pressures up to 250 psi, even after repeated use.
- NASA uses ORFS connectors in hypersonic test facilities, where they withstand temperatures over 3000°F and high flow rates.
- Naval and industrial gas systems rely on ORFS connectors for pressures up to 6000 psi, ensuring safety and reliability.
- Gas plants use them to contain helium, a gas that is hard to seal, at pressures up to 3000 psi.
- High-pressure CO₂ refrigeration systems use ORFS connectors to stay leak-free under tough conditions.
ORFS connectors offer leak-proof performance in many demanding factory and industrial settings.
NPTF (National Pipe Taper Fuel) Connectors
NPTF connectors use tapered threads to create a tight, leak-free seal.
- These connectors handle pressures from 6,000 to 10,000 psi and higher.
- They meet standards like ASME B16.11 and ASME B31.3 for safety and reliability.
- NPTF connectors use strong materials and precise machining to prevent leaks under pressure and vibration.
- Factories use NPTF connectors in oil and gas, chemical processing, hydraulic systems, and manufacturing equipment.
NPTF threads create a mechanical fit that seals without extra sealants. This makes them ideal for high-pressure hydraulic hose connector applications where leak prevention is critical.
NPSM (National Pipe Straight Mechanical) Connectors
NPSM connectors use straight threads and need extra sealing parts, such as O-rings or gaskets.
| Aspect | NPSM Connectors | NPT Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | Straight (non-tapered) | Tapered (wedging effect for sealing) |
| Sealing Mechanism | Needs O-rings or gaskets | Self-sealing with thread deformation |
| Pressure Capability | Up to 6,000 PSI with proper sealing | Up to 10,000+ PSI with sealants |
| Application Suitability | Good for frequent disassembly and alignment | Best for permanent, high-pressure installations |
NPSM connectors work well when workers need to take fittings apart often or need precise alignment. Their performance depends on the quality of the sealing components.
NPSM connectors follow ANSI and ASME standards, which help ensure reliable mechanical connections in factory systems.
BSP (British Standard Pipe) Connectors
BSP connectors follow British and international standards, such as ISO 7 and ISO 228.
- BSPT (tapered) threads seal by thread distortion, while BSPP (parallel) threads use O-rings or washers for sealing.
- Factories use BSP connectors in construction, agriculture, manufacturing, and oil and gas.
- BSP connectors pass strict tests, including proof pressure, burst pressure, and cyclic endurance tests.
- Certification bodies require product testing, quality checks, and factory audits to ensure safety.
BSP connectors provide secure, leak-resistant connections in hydraulic hose connector systems. Their design supports high-pressure use and helps reduce system failures and downtime.
Proper installation and maintenance help BSP connectors deliver reliable performance in demanding factory environments.
Pros, Cons, and Applications of Hydraulic Hose Connectors in Factories
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Type
Different hydraulic hose connectors offer unique benefits and drawbacks. JIC connectors provide reliable performance in high-pressure systems and see wide use in North America. They require precise flare contact to prevent leaks. BSP connectors work well worldwide and come in both parallel and tapered designs, making them versatile. ORFS connectors use an O-ring for superior leak protection, but their sealing mechanism is more complex. NPT connectors are common in North American plumbing but do not perform as well in high-pressure situations.
Material choice also affects performance. Stainless steel connectors resist corrosion and work best in harsh environments, while carbon steel offers high strength at a lower cost but may corrode without coating. Aluminum connectors are lightweight and resist corrosion but cost more than carbon steel.
Push-lock and push-to-connect fittings allow for quick, tool-free installation but only suit low or medium pressure. Crimp and flare fittings provide strong, leak-proof seals for high-pressure use but require special tools.
Typical Industrial Applications
Factories select hydraulic hose connectors based on system needs. JIC connectors often appear in industrial and automotive hydraulic systems. BSP connectors serve in hydraulic and pneumatic systems worldwide. ORFS connectors fit high-pressure hydraulic systems, such as those in aerospace or heavy machinery. NPT connectors work best in low-pressure plumbing or hydraulic systems.
NPSM connectors help reduce hose twisting and strain during assembly, making them useful for frequent disassembly. Stainless steel connectors protect against saltwater and chemicals, so factories use them in marine and chemical processing. Push-to-connect fittings make sense for automotive and light machinery, where quick changes are needed.
Choosing the right hydraulic hose connector improves safety, reduces downtime, and ensures reliable operation in factory environments.
Practical Guide to Matching Hydraulic Hose Connectors to Factory Needs

Identifying System Requirements
Factories must first understand their system’s needs before choosing a hydraulic hose connector. The S.T.A.M.P.E.D. method helps with this process. It stands for Size, Temperature, Application, Material, Pressure, Ends, and Delivery. Each factor affects connector choice. For example, the size and pressure rating must match the system to avoid leaks. Temperature and material compatibility prevent hose damage. Application and delivery needs guide the selection of ends and fittings. This method ensures the connector will work safely and efficiently.
Ensuring Compatibility and Safety
Compatibility and safety are top priorities in hydraulic systems. Factories should always match connectors to the fluid type and pressure rating. Cleanliness is important. Workers should keep tubing and fittings free from dirt to prevent leaks. Correct alignment reduces stress on hoses. Following torque specifications helps prevent cracks and leaks. Pressure tests confirm that connections hold under working conditions. Regular inspections for wear, cracks, or leaks help maintain system safety.
Proper selection and installation of hydraulic quick couplings can reduce system failures by 30% and lower fluid leaks by up to 15%, according to industry reports.
Tips for Selection and Installation
- Use the S.T.A.M.P.E.D. method to select hoses and connectors.
- Handle and store hoses carefully to avoid kinks, cuts, or UV damage.
- Wear gloves and safety glasses during installation.
- Secure hoses with clamps or brackets to prevent movement.
- Avoid overtightening fittings to prevent cracks.
- Do not mix old and new hoses or use hoses that are too short.
- Inspect hoses regularly and replace damaged ones quickly.
A step-by-step approach helps ensure a safe and reliable hydraulic hose connector installation. Factories that follow these tips see fewer leaks and longer equipment life.
Quick-Reference Table and Checklist for Hydraulic Hose Connector Selection
Connector Selection Table
The table below helps users compare important features when choosing connectors for factory systems. Each metric affects how well the connector works in different situations.
| Metric | What It Means | Why It Matters for Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Inside Diameter (I.D.) | The size of the hose opening, measured in 1/16″ steps | A correct size keeps pressure steady and avoids flow problems |
| Outer Diameter (O.D.) | The total width of the hose, including the wall | Ensures the hose fits in tight spaces and matches clamps |
| Hose Length | The distance from one end of the hose to the other, including fittings | Longer hoses can lower pressure, so length affects performance |
| Flow Rate | How much fluid moves through the hose each minute | Picking the right size prevents slowdowns and keeps systems safe |
Tip: Always check these measurements before buying or installing a new connector. This helps prevent leaks and keeps machines running smoothly.
Decision-Making Checklist
Use this checklist to make sure the connector matches your factory’s needs:
- Measure the inside and outside diameter of the hose
- Check the length needed for the system layout
- Confirm the flow rate required by the equipment
- Match the connector type to the system’s pressure rating
- Make sure the material fits the working environment (like temperature or chemicals)
- Look for industry standards or certifications
- Inspect all parts for damage before installation
- Test the connection after setup to check for leaks
Following this checklist helps factories avoid mistakes and keeps workers safe.
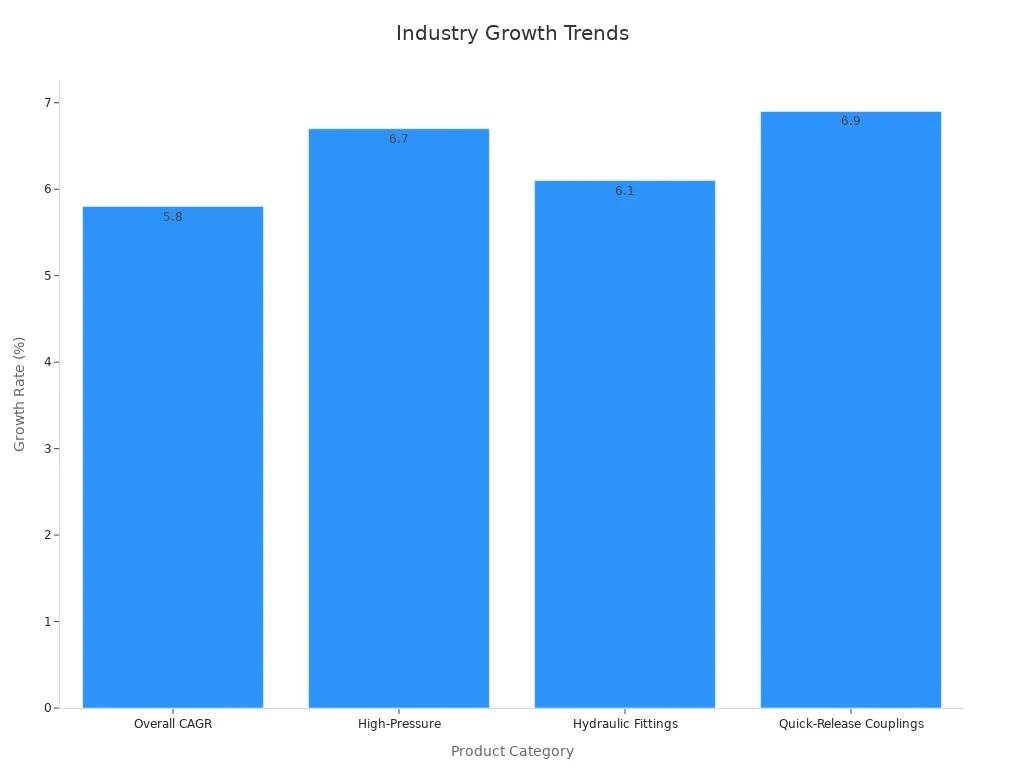
Factories select ORFS, JIC, SAE, NPTF, NPSM, and BSP connectors for their unique strengths. Industry growth, especially in Asia Pacific, highlights the need for reliable hydraulic hose connector choices.
Using the checklist and table helps decision-makers ensure safety and efficiency.
FAQ
What is the main reason factories choose stainless steel connectors?
Stainless steel connectors resist rust and corrosion. They last longer in harsh environments. Factories use them to keep systems safe and reliable.
How often should workers inspect hydraulic hose connectors?
Workers should inspect connectors every month. Regular checks help find leaks or damage early. This keeps the system safe and running well.
Can different connector types work together in one system?
| Connector Type | Compatibility |
|---|---|
| JIC & SAE | Often Yes |
| NPTF & BSP | Usually No |
Mixing types can cause leaks. Always check compatibility before use.
Post time: Jun-19-2025
