
Choosing the right hydraulic hose fittings keeps equipment running smoothly. Studies reveal that improper fitting selection causes about 10% of total equipment downtime. When someone matches a hose adapter to a rubber hose or chooses stainless steel fittings for harsh conditions, they reduce leaks and failures. Reliable fittings save time and money.
Key Takeaways
- Always match hydraulic hose fittings to your equipment’s size, pressure, and fluid needs to prevent leaks and downtime.
- Choose fitting materials that suit your environment and job conditions to ensure durability and safety.
- Follow proper installation and regular inspection routines to keep hydraulic systems running smoothly and avoid costly failures.
Identify Equipment Requirements for Hydraulic Hose Fittings
Choosing the right hydraulic hose fittings starts with understanding what the equipment needs. Every machine has its own set of requirements, and missing even one detail can lead to leaks, breakdowns, or expensive downtime. Let’s break down the key steps.
Check Manufacturer Specifications
Manufacturers know their equipment best. They provide detailed specifications for hoses and fittings, including size, type, and material. These specs help users avoid mismatches that can cause failures.
Tip: Always keep the equipment manual handy. It lists the recommended hydraulic hose fittings and explains how to check for wear or damage.
Recent surveys show that equipment requirements can change a lot depending on the job site. For example:
- Some sites use backhoes with special grapplers for handling drums.
- Others add splash shields or switch to foam tires to handle sharp debris.
- Propane-powered loaders help reduce fumes indoors.
- Contractors often rent or modify equipment to fit unique tasks.
Manufacturers like Allied Steel & Tractor Products and Ingersoll-Rand Co. offer a wide range of hydraulic equipment. Even with all these differences, many sites end up using similar types of machines and fittings.
Following the manufacturer’s guidelines helps reduce failure rates. Regular inspections, fluid checks, and using the right parts all play a role in keeping systems running smoothly.
Determine Pressure Ratings
Pressure ratings matter a lot in hydraulic systems. Using a fitting that can’t handle the pressure can lead to leaks or bursts.
Here’s a quick look at typical pressure ratings for different applications:
| Hose Pressure Category | Typical Pressure Range (PSI) | Common Reinforcement Type | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Pressure | Below 250 | Textile/fabric braid | Low-pressure hydraulic systems |
| Medium Pressure | Up to 3,000 | Wire braid | Dump trucks, farm equipment, plows |
| High Pressure | 3,000 – 6,000 | Wire braid and spiral braid | Mining, oil and gas, cranes |
Note: Always choose hydraulic hose fittings that exceed the system’s maximum pressure. This adds a safety margin and helps prevent accidents.
In industries like agriculture and construction, machines often work under high pressure. Tractors, excavators, and cranes need fittings that can handle thousands of PSI. Picking the right pressure rating keeps equipment safe and reliable.
Assess Fluid Compatibility
Not all hydraulic fluids are the same. Some contain special additives or contaminants that can react with hose materials. If the fitting or hose material isn’t compatible with the fluid, it can break down, swell, or leak.
To make sure everything works together:
- Identify the type of hydraulic fluid in use, including any additives.
- Check compatibility charts from the manufacturer. These charts show which materials work with which fluids.
- If unsure, test the hose material with the fluid before using it in the field.
- Think about long-term effects. Some fluids can change over time and affect compatibility.
- Review technical data sheets for details on pressure, temperature, and material limits.
- Ask manufacturer experts for advice if the situation is complex.
- Follow industry standards to keep everything safe and legal.
Choosing the right hydraulic hose fittings and materials for the fluid in use helps prevent leaks and extends the life of the system.
Hydraulic Hose Fittings Types and Sizes

Common Fitting Types
Hydraulic hose fittings come in several types, each designed for specific uses. The most common types include threaded connectors, quick connect/disconnect connectors, flanged connectors, and compression connectors. Industry reports show that mobile hydraulic fittings make up about 60% of the market, especially in construction and agriculture. While detailed numbers for each fitting type are not public, these categories cover most needs on job sites. Threaded connectors are popular because they create a strong seal. Quick connect fittings help workers save time during repairs or equipment changes. Flanged and compression connectors work well in high-pressure or vibration-heavy environments.
Measuring Hose and Fitting Sizes
Getting the right size matters for safety and performance. Hose assemblies are measured by overall length, from end to end. For O-ring face seal ends, measure from the sealing face. For angled fittings, measure at the centerline of the sealing surface. NAHAD standards set clear tolerances:
- Up to 12 inches: ±1/8 inch
- 12 to 18 inches: ±3/16 inch
- 18 to 36 inches: ±1/4 inch
- Over 36 inches: ±1% of overall length
After crimping, hoses can grow in length, so always check measurements after assembly. Fitting sizes and thread dimensions follow standards like ASME B1.1 and ISO 261. Tools like calipers and thread pitch gauges help ensure accuracy.
Thread Types and Standards
Thread type plays a big role in choosing the right hydraulic hose fittings. Many thread types exist, and each fits certain regions or industries. Here’s a quick look:
| Thread Type | Common Usage/Region | Notes | Standards Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | U.S. industrial | Tapered thread, strong seal | ASME B1.20.1 |
| BSPP/BSPT | Commonwealth countries | BSPP is parallel, BSPT tapered | ISO 7 |
| Metric Parallel | Metric system countries | Parallel thread | ISO 724 |
| UTS | U.S. and international | Washer seal | ASME B1.1 |
NPT threads are very common in the U.S., while BSPP and BSPT are used in Australia and the UK. Metric threads show up in Europe and Asia. Identifying the right thread can be tricky because some look similar. When in doubt, ask an expert or use a thread gauge.
Material Selection for Hydraulic Hose Fittings
Material Options
Choosing the right material for hydraulic hose fittings makes a big difference in how well a system works. Each material has strengths and weaknesses.
- Carbon steel fittings handle high pressure and offer strong durability. They need protective coatings to prevent rust.
- Stainless steel fittings resist corrosion and work well in harsh environments, but they cost more.
- Brass fittings provide moderate strength and resist corrosion, making them good for lower pressure jobs.
- Forged fittings are stronger and less likely to leak than brazed ones.
- Plating thickness matters. Too much plating can flake off, while too little leads to leaks and rust.
Industry standards like SAE and ASTM set rules for pressure and corrosion resistance. The right choice depends on the job, the fluid, and the environment.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion can ruin hydraulic hose fittings quickly, especially in tough environments. Studies show that stainless steel with higher chromium, nickel, and molybdenum levels stands up better to salt and chemicals. Bright-annealed stainless steel keeps a smooth, shiny surface and resists pitting, even after a year in marine air.
Note: Special heat treatments and alloy mixes help fittings last longer in places with lots of moisture or chemicals.
Coatings like zinc or zinc-nickel protect carbon steel, but some coatings face environmental limits. Always check if the fitting meets or beats industry salt spray tests.
Application Suitability
Not every material fits every job. For example, carbon steel works best in high-pressure systems, while brass fits low-pressure, low-temperature uses. Stainless steel shines in places with lots of vibration, heat, or chemicals.
Manufacturers test materials for wear, strength, and how they handle different fluids. A mobile crane company once picked a special valve material after testing it for flow, pressure, and control. The right match keeps systems safe and reliable.
Environmental and Safety Considerations for Hydraulic Hose Fittings
Temperature Range
Temperature changes can affect how well hydraulic hose fittings work. Each material handles heat and cold differently. For example, carbon steel works best from -40°C to +100°C, while stainless steel can handle much higher temperatures. Brass and aluminum have their own limits. When temperatures rise above normal, the pressure rating drops. This means fittings might not hold as much pressure when it gets hot.
| Material | Safe Temperature Range (°C) | Pressure Derating at High Temps |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | -40 to +100 | Pressure drops above +38°C |
| Stainless Steel | -54 to +200 | Keeps high pressure at higher temperatures |
| Brass | -53 to +204 | Moderate pressure drop |
| Aluminum | -40 to +100 | Not safe above +100°C |
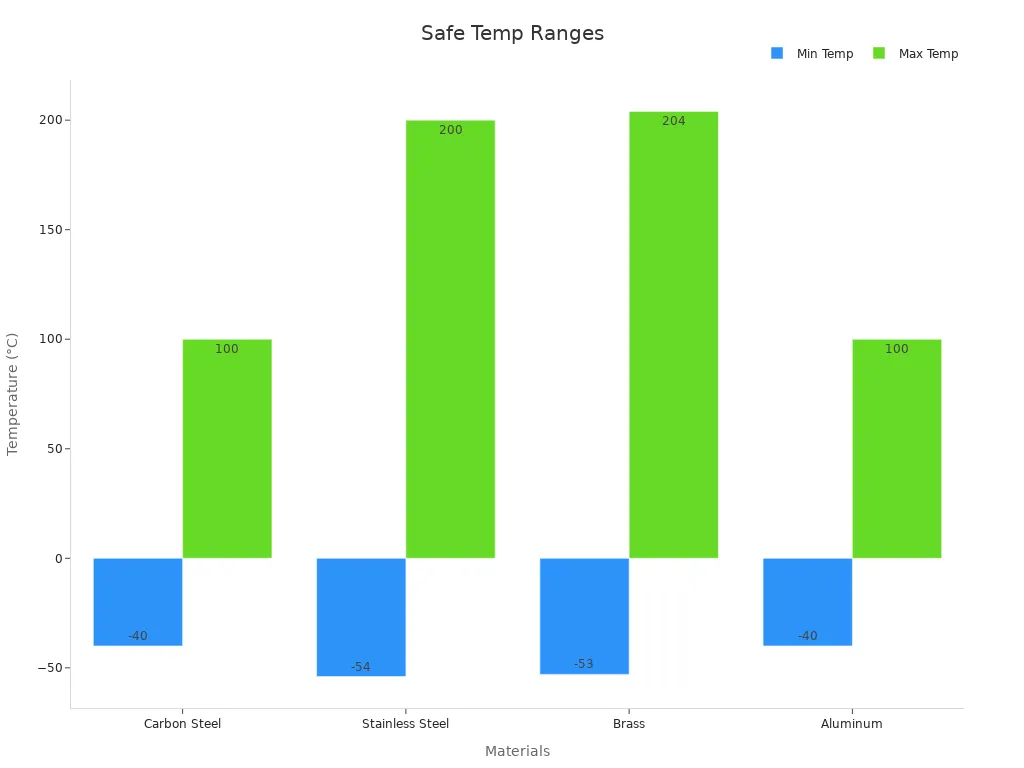
Choosing the right material helps prevent leaks and failures in extreme weather.
Vibration and Movement
Machines often shake or move during work. Vibration can loosen fittings, cause cracks, or make seals fail. Over time, this leads to leaks or even hose bursts. To fight these problems, many companies use special fittings with locking threads or O-ring face seals. They also use clamps, flexible hoses, and good hose routing to reduce stress. Swivel adapters help stop hoses from twisting. These steps keep the system safe and working longer.
- Vibration can shorten hose life.
- Testing for vibration helps spot problems early.
- Clamps and supports reduce movement and damage.
- Good installation stops leaks and failures.
Safety Standards
Following safety rules keeps workers and equipment safe. Studies show that almost all hydraulic failures can be prevented with good maintenance and training. Companies use many safety steps:
- Train operators and technicians.
- Inspect systems often.
- Use emergency shutdown plans.
- Add safety guards and barriers.
- Check fluids and replace them on schedule.
- Use sensors for real-time safety checks.
- Wear personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Track and report safety issues.
- Keep training up to date.
When companies follow these standards, they see fewer failures, less downtime, and lower costs. Premium components also help by reducing leaks and environmental harm. In industries like forestry, using better fittings can save thousands of dollars each year and protect the environment.
Installation and Maintenance of Hydraulic Hose Fittings
Proper Assembly
Proper assembly keeps hydraulic systems safe and leak-free. When technicians use the right torque, they prevent leaks and damage. Over-tightening or under-tightening can cause hose failure and increase downtime. The Torque Wrench Method helps apply the correct force every time. This method gives precise and consistent results.
Tip: Secure connections with the right torque extend the life of both hoses and fittings.
A few key points to remember:
- Correct torque stops fluid loss and keeps pressure steady.
- Good assembly lowers maintenance costs.
- Secure fittings reduce safety risks and sudden equipment stops.
Inspection and Replacement
Regular checks help spot problems before they grow. Following a set schedule keeps equipment running longer.
- Stick to the manufacturer’s maintenance plan.
- Check hydraulic fluid often and test for dirt or wear.
- Change filters on time or when tests show it is needed.
- Use only high-quality replacement parts.
- Look closely at hoses and fittings for leaks or damage.
- Use preventive maintenance to catch issues early.
- Keep records of all checks and repairs.
These steps help prevent failures and save money over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many problems start with small mistakes during installation or maintenance.
- Improper crimping or using the wrong fittings can cause hoses to fail fast.
- Untrained workers or old tools increase the risk of bad assembly.
- Mismatched hose and fitting types lower safety.
- Poor alignment leads to twisting and stress.
- Skipping inspections lets damage go unnoticed.
- Repairing instead of replacing damaged hoses is risky.
- Mixing parts from different brands can cause leaks.
- Over-tightening fittings may crack or break them.
- Using hoses that are too short puts extra tension on the system.
Note: Always wear safety gear and follow the latest standards when working with hydraulic hose fittings.
Choosing the right hydraulic hose fittings means matching size, type, and material to the job. Exceeding system ratings and checking compatibility keeps equipment safe and efficient. For tough jobs, they should talk to a hydraulic expert. Good fitting selection protects hoses, prevents leaks, and helps machines last longer.
FAQ
What happens if someone uses the wrong hydraulic fitting size?
The wrong size can cause leaks or hose bursts. Equipment may stop working. Always check the size before installing a new fitting.
How often should a person inspect hydraulic hose fittings?
A person should check fittings every month. Look for leaks, cracks, or rust. Early checks help prevent bigger problems.
Can different brands of hose fittings work together?
- Mixing brands may cause leaks or poor fit.
- Always use fittings from the same brand for best results.
- Check manufacturer guidelines before mixing.
Post time: Jun-26-2025
